

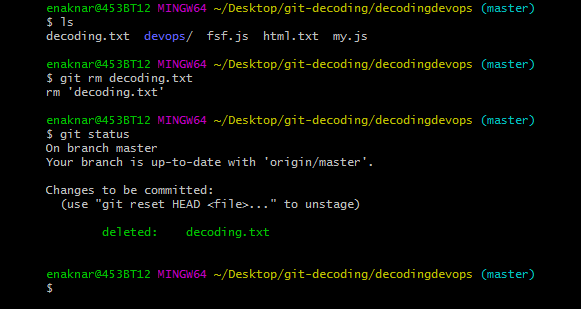
OR git branch -d feature-register (Shorter version) Here are the steps to delete a git branch locally. Git branch deletion is an essential task when working with git repositories. Tip: Always make sure to have a meaningful branch name of the git repo. Now, you have moved into the master branch and want to delete the feature-register branch. Open a command line tool and run: git checkout master You have completed the feature and now want to merge it. You are working on a feature-register branch. Once the main features are complete, all developers need to merge their branch into the master branch. Let's say a repository has a master or main branch. You will always need to checkout from the branch you want to delete. Suppose you want to delete any git branch, whether locally or remotely. So once you've mastered this simple tutorial, you'll be able to delete any git branch with ease!
#Git remove local branch how to
Then, I will demonstrate how to delete a git branch remotely using the git push command.įinally, you will learn the benefits of using these commands and some best practices for remote deletion. No problem! This simple tutorial will teach you how to do both in just minutes.įirst, you will learn how to delete a local git branch locally. I did fast-forward merges on remote with many branches, and when I ran git branch -merged locally, it didn't show me any merged branches.Are you working on a git repository and want to delete a git branch locally?ĭo you need to delete a git branch remotely but don't know how to do that? The same might also happen is you do a fast-forward merged. In pull request cases where you do a different merge (for example, a squash merge), the branch history is altered and as a result git branch -merged will not show locally merged branches.
When you create a local branch, say "header", a new file in the project. How do you solve this? First, we need to understand how local and remote branches work together.
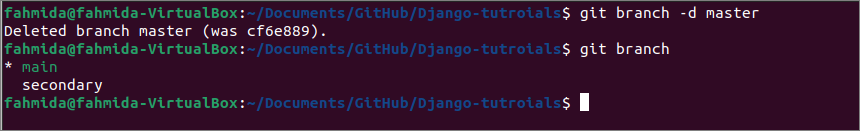
Repeating this for many other branches leaves you with many outdated local branches.
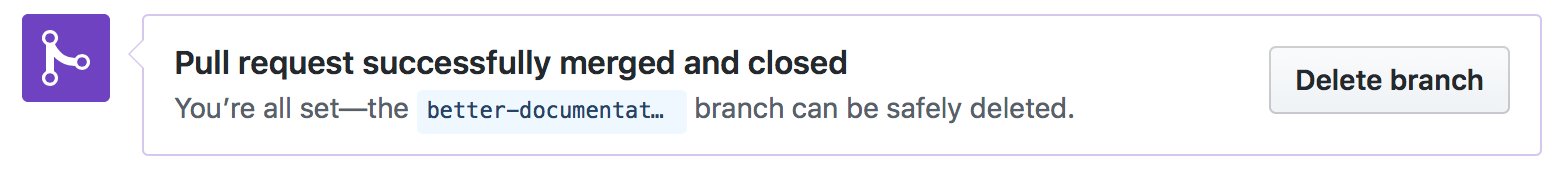
When you do this, you may forget to delete the local branch. On merging that branch, the branch becomes irrelevant, and GitHub, for example, gives you the option to delete the branch afterward. And when you're done with all the necessary changes for that branch, you would merge the branch to your production branch (like master). When you create a local branch, most of the time, you would push the changes in that branch to a branch of the same name in the remote repository. But, the more branches you have, the more difficult they are to manage. The idea of branches in git is a nice feature as it allows to work on separate parts of a project simultaneously.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
